OOPS! You forgot to upload swfobject.js ! You must upload this file for your form to work.
Rice University offered its version of the resistive memory
![]()
|
xtreview is your : Video card - cpu - memory - Hard drive - power supply unit source |
|
|||
|
|
||||
 Recommended : Free unlimited image hosting with image editor
Recommended : Free unlimited image hosting with image editor
|
POSTER: computer news || RICE UNIVERSITY OFFERED ITS VERSION OF THE RESISTIVE MEMORY |
DATE:2014-07-27 |
|
|
Resistive memory or ReRAM (RRAM) has a lot of options for practical implementation, although its overall design is quite simple and consists of two crossed electrodes, between which are localized areas (cells) with a controlled variable resistor. Supplying current to the electrodes of different polarity can increase or decrease the resistance, thereby recording a cell specific bit of data. Moreover, the resistance of the cell can generate a large number of gradations, which significantly increases
the number stored in each data bit cell.  Among other developers, often occurs HP memristor . University group proposed to use as a dielectric between the control electrodes of specially treated silica. During processing, dielectric acquires a porous structure, whereupon the surface is applied to both sides of the grid formed by the electrodes and the cell area. 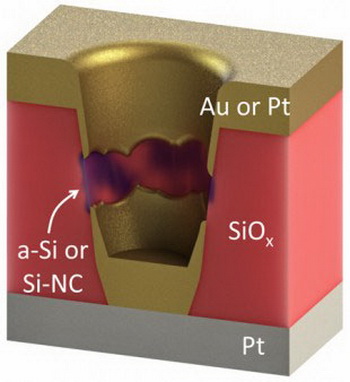 Supply voltage to the electrodes causes the pores in front of the contact groups occurrence of crystalline conductive filaments. From the magnitude of the current will depend on number of filaments, and therefore, resulting in resistance of the small current in the read mode. According to the developers, their version of ReRAM cell can record up to nine bits of data, which is a record of all existing options resistive memory. The scientists also believe in 100-fold superiority developed ReRAM options in terms of increasing the number of write cycles. Finally, the voltage value in the recording mode of only 2 volts, which is 13 times less than the voltage value in the case of competing designs. On the problem of creating an inexpensive and effective ReRAM memory group at Rice University has around five years. At the same time there are reports that some of the non-volatile memory manufacturers interested in this particular technology. Related Products : | ||
|
|
||
|
xtreview is your : Video card - cpu - memory - Hard drive - power supply unit source |
|
|
|
|
||
|
Xtreview Support  N-Post:xxxx Xtreview Support        |
RICE UNIVERSITY OFFERED ITS VERSION OF THE RESISTIVE MEMORY |
| Please Feel Free to write any Comment; Thanks  |
The Moscow State University created a program to detect error causing headaches in 3D-scenes (2016-03-01)
NVIDIA and Stanford University will secure head-mounted display (2015-11-23)
Rice University offered its version of the resistive memory (2014-07-27)
Michigan University released a new type of monitor (2013-02-08)
University of Austin Portable projectors (2012-01-25)
university of North Carolina propose a new solution to increase the performance of multi core processors (2011-05-28)
![]()
To figure out your best laptops .Welcome to XTreview.com. Here u can find a complete computer hardware guide and laptop rating .More than 500 reviews of modern PC to understand the basic architecture


7600gt review
7600gt is the middle card range.
We already benchmarked this video card and found that ...

 geforce 8800gtx and 8800gts
geforce 8800gtx and 8800gts  Xtreview software download Section
Xtreview software download Section  AMD TURION 64 X2 REVIEW
AMD TURION 64 X2 REVIEW  INTEL PENTIUM D 920 , INTEL PENTIUM D 930
INTEL PENTIUM D 920 , INTEL PENTIUM D 930  6800XT REVIEW
6800XT REVIEW  computer hardware REVIEW
computer hardware REVIEW  INTEL CONROE CORE DUO 2 REVIEW VS AMD AM2
INTEL CONROE CORE DUO 2 REVIEW VS AMD AM2  INTEL PENTIUM D 805 INTEL D805
INTEL PENTIUM D 805 INTEL D805  Free desktop wallpaper
Free desktop wallpaper  online fighting game
online fighting game  Xtreview price comparison center
Xtreview price comparison center Lastest 15 Reviews


Rss Feeds
Last News
- The new version of GPU-Z finally kills the belief in the miracle of Vega transformation
- The motherboard manufacturer confirms the characteristics of the processors Coffee Lake
- We are looking for copper coolers on NVIDIA Volta computing accelerators
- Unofficially about Intels plans to release 300-series chipset
- The Japanese representation of AMD offered monetary compensation to the first buyers of Ryzen Threadripper
- This year will not be released more than 45 million motherboards
- TSMC denies the presentation of charges from the antimonopoly authorities
- Radeon RX Vega 64 at frequencies 1802-1000 MHz updated the record GPUPI 1B
- AMD itself would like to believe that mobile processors Ryzen have already been released
- AMD Vega 20 will find application in accelerating computations
- Pre-orders for new iPhone start next week
- Radeon RX Vega 57, 58 and 59: the wonders of transformation
- ASML starts commercial delivery of EUV-scanners
- The older Skylake processors with a free multiplier are removed from production
- Meizu will release Android-smartphone based on Helio P40
- AMD Bristol Ridge processors are also available in American retail
- The fate of Toshiba Memory can be solved to the next environment
- duo GeForce GTX 1080 Ti in GPUPI 1B at frequencies of 2480-10320 MHz
- New Kentsfield overclocking record up to 5204 MHz
- Lenovo released Android-smartphone K8

HALO 3 HALO 3 - Final Fight!

PREY Prey is something you don t often see anymore: a totally unigue shooter experience.

computer news computer parts review Old Forum Downloads New Forum Login Join Articles terms Hardware blog Sitemap Get Freebies


